最近因为工作需要,学习了一段时间Netty的源码,并做了一个简单的分享,研究还不是特别深入,继续努力。因为分享也不涉及公司业务,所以这里也把这次对源码的研究成果分享出来以下都是在游戏服务器开发中针对Netty使用需要了解知识点以及相关优化
这次分享主要设计以下内容
Netty线程模型
Netty对TCP相关参数的配置和具体含义
Netty对Epoll的封装
Netty的优雅关闭
一、Reactor模式和Netty线程模型 客户端连接数的限制
内存资源
CPU资源
端口号资源1 cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range
文件描述符资源1 2 3 系统级:当前系统可打开的最大数量,通过 cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max 查看 用户级:指定用户可打开的最大数量,通过 cat /etc/security/limits.conf 查看 进程级:单个进程可打开的最大数量,通过 cat /proc/sys/fs/nr_open 查看
线程资源
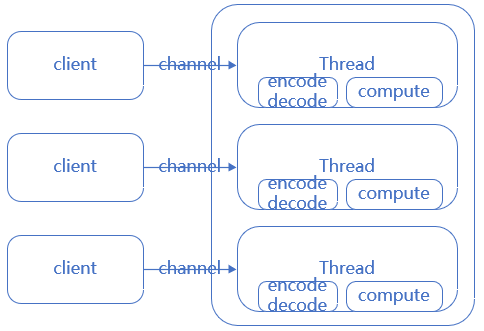
1. BIO模型
所有操作都是同步阻塞(accept,read)
客户端连接数与服务器线程数比例是1:1
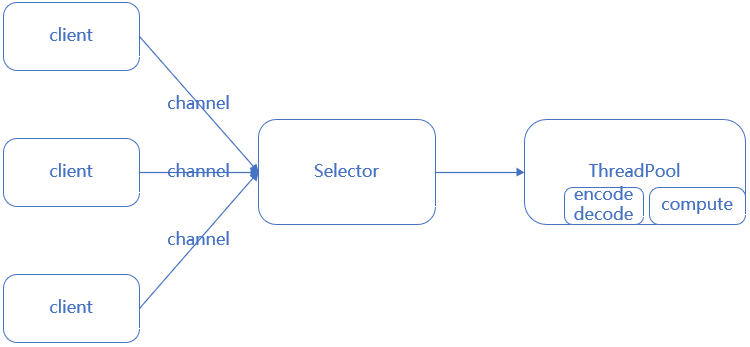
2. NIO模型
非阻塞IO
通过selector实现可以一个线程管理多个连接
通过selector的事件注册(OP_READ/OP_WRITE/OP_CONNECT/OP_ACCEPT),处理自己感兴趣的事件
客户端连接数与服务器线程数比例是n:1
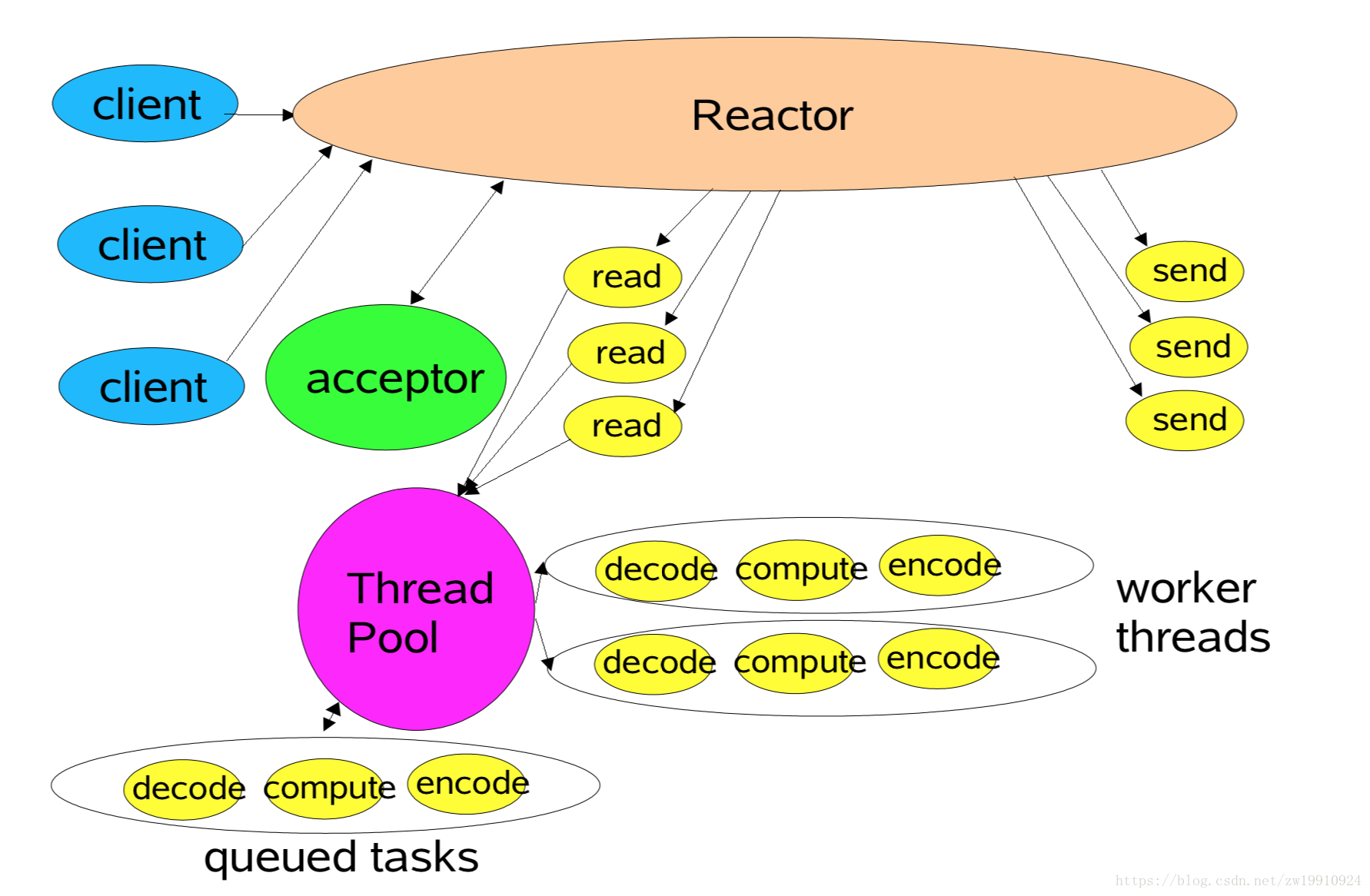
3. Reacor模型 ①. 单Reacor单线程模型 所有IO在同一个NIO线程完成(处理连接,分派请求,编码,解码,逻辑运算,发送)
优点 :
缺点 :
单线程处理大量链路时,性能无法支撑,不能合理利用多核处理
线程过载后,处理速度变慢,会导致消息积压
一旦线程挂掉,整个通信层不可用redis使用的就是reactor单进程模型,redis由于都是内存级操作,所以使用此模式没什么问题
reactor单线程模型图 :
netty reactor单线程模型图 :
Netty对应实现方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 EventLoopGroup ioGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); b.group(ioGroup, ioGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(initializer); ChannelFuture f = b.bind(portNumner); cf = f.sync(); f.get();
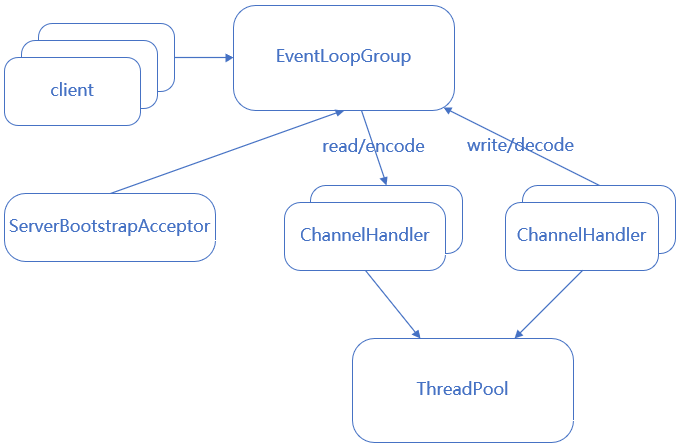
②. 单Reactor多线程模型 根据单线程模型,io处理中最耗时的编码,解码,逻辑运算等cpu消耗较多的部分,可提取出来使用多线程实现,并充分利用多核cpu的优势
优点 :
缺点 :
对于单Reactor来说,大量链接的IO事件处理依然是性能瓶颈
reactor多线程模型图 :netty reactor多线程模型图 :
Netty对应实现方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 EventLoopGroup ioGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); b.group(ioGroup, ioGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(initializer); ChannelFuture f = b.bind(portNumner); cf = f.sync(); f.get();
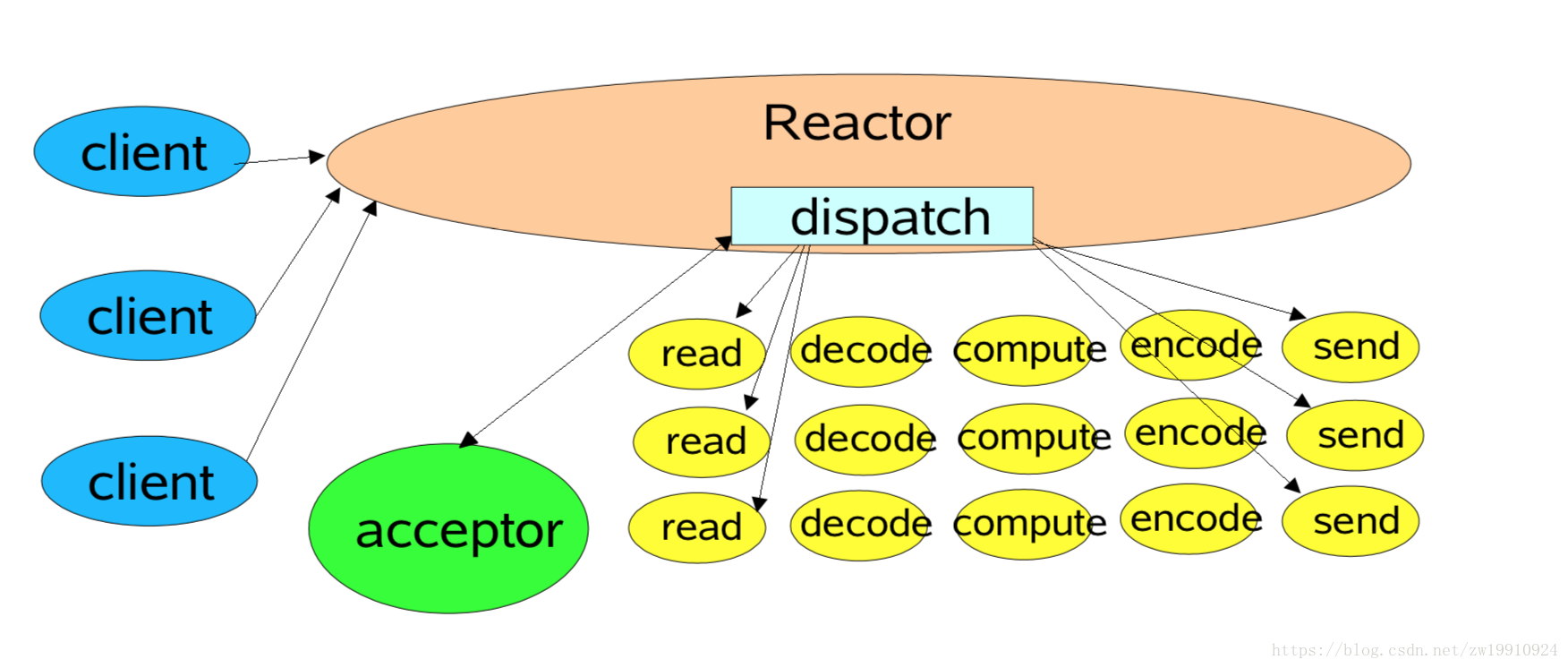
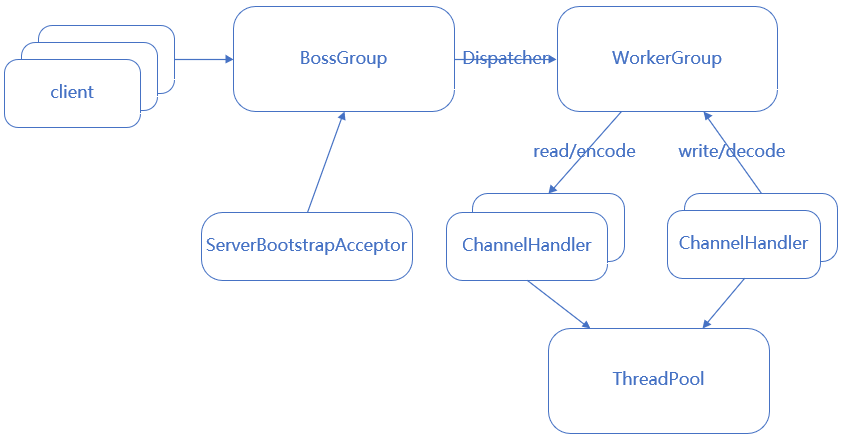
③. 主从Reactor多线程模型 根据多线程模型,可把它的性能瓶颈做进一步优化,即把reactor由单个改为reactor线程池,把原来的reactor分为mainReactor和subReactor
优点 :
解决单Reactor的性能瓶颈问题(Netty/Nginx采用这种设计)
reactor主从多线程模型图 :
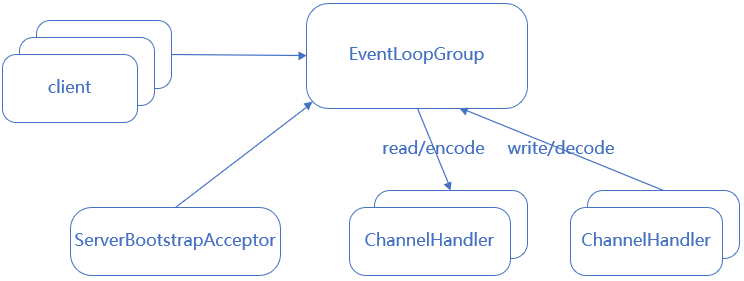
netty reactor主从多线程模型图 :
Netty对应实现方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(initializer); ChannelFuture f = b.bind(portNumner); cf = f.sync(); f.get();
④. 部分源码分析
创建group实例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 super (nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS;static { DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1 , SystemPropertyUtil.getInt( "io.netty.eventLoopThreads" , NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2 )); } public NioEventLoopGroup (int nThreads, Executor executor) this (nThreads, executor, SelectorProvider.provider()); } EventExecutorChooserFactory.EventExecutorChooser chooser; children = new EventExecutor[nThreads]; for (int i = 0 ; i < nThreads; i ++) { children[i] = newChild(executor, args); } chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);
设置group
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Override public ServerBootstrap group (EventLoopGroup group) return group(group, group); } ServerBootstrap.group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup){ }
Netty启动
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 ServerBootstrap:bind() -> doBind() -> initAndRegister() private ChannelFuture doBind (final SocketAddress localAddress) final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister(); doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise); } final ChannelFuture initAndRegister () Channel channel = channelFactory.newChannel(); ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel); }
由以上源码可得知,bind只在起服调用一次,因此bossGroup仅调用一次regist,也就是仅调用一次next,因此只有一根线程是有用的,其余线程都是废弃的,所以bossGroup线程数设置为1即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 private static void doBind0 ( final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run () if (regFuture.isSuccess()) { channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE); } else { promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause()); } } }); }
客户端连接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 NioEventLoop.run() -> processSelectedKeys() -> ... -> ServerBootstrapAcceptor.channelRead public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler); setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger); setAttributes(child, childAttrs); childGroup.register(child) }
二、select/poll和epoll 1.概念
select(时间复杂度O(n)):用一个fd数组保存所有的socket,然后通过死循环遍历调用操作系统的select方法找到就绪的fd
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 while (1 ) { nready = select(list); for (fd <-- fdlist) { if (fd != -1 ) { read(fd, buf); if (--nready == 0 ) break ; } } }
poll(时间复杂度O(n)):同select,不过把fd数组换成了fd链表,去掉了fd最大连接数(1024个)的数量限制
epoll(时间复杂度O(1)):解决了select/poll的几个缺陷
调用需传入整个fd数组或fd链表,需要拷贝数据到内核
内核层需要遍历检查文件描述符的就绪状态
内核仅返回可读文件描述符个数,用户仍需自己遍历所有fd
epoll是操作系统基于事件关联fd,做了以下优化:
内核中保存一份文件描述符集合,无需用户每次都重新传入,只需告诉内核修改的部分即可。(epoll_ctl)
内核不再通过轮询的方式找到就绪的文件描述符,而是通过异步 IO 事件唤醒。(epoll_wait)
内核仅会将有 IO 事件的文件描述符返回给用户,用户也无需遍历整个文件描述符集合。
epoll仅在Linux系统上支持
2.jdk提供selector 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public static SelectorProvider create () return new WindowsSelectorProvider(); } public static SelectorProvider create () String str = (String)AccessController.doPrivileged(new GetPropertyAction("os.name" )); if (str.equals("SunOS" )) { return createProvider("sun.nio.ch.DevPollSelectorProvider" ); } if (str.equals("Linux" )) { return createProvider("sun.nio.ch.EPollSelectorProvider" ); } return new PollSelectorProvider(); }
3.Netty提供的Epoll封装 netty依然基于epoll做了一层封装,主要做了以下事情:
(1)java的nio默认使用水平触发,Netty的Epoll默认使用边缘触发,且可配置
边缘触发:当状态变化时才会发生io事件。
水平触发:只要满足条件,就触发一个事件(只要有数据没有被获取,内核就不断通知你)
(2)Netty的Epoll提供更多的nio的可配参数。
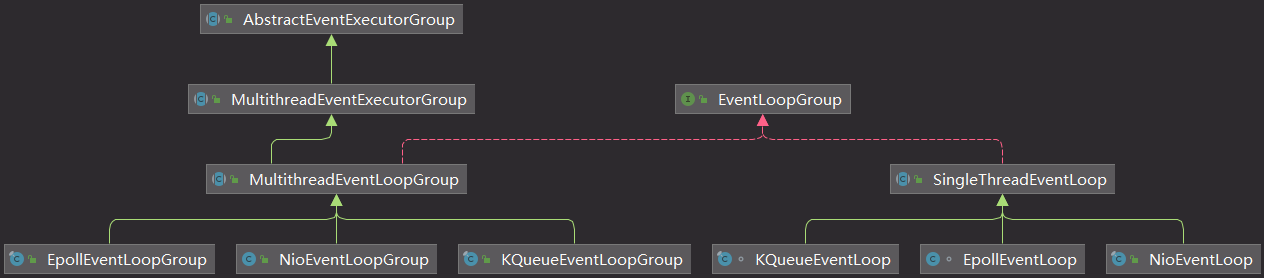
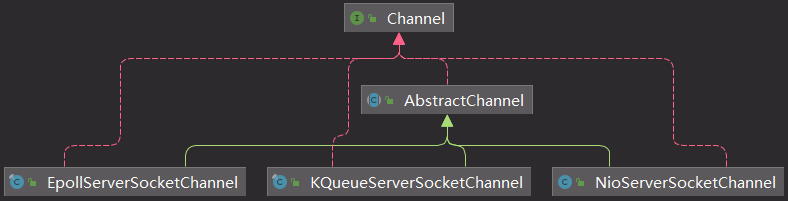
4.Netty相关类图
线程组类图
channel类图
5.配置Netty为EpollEventLoop 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 bossGroup = new EpollEventLoopGroup(1 , new DefaultThreadFactory("BOSS_LOOP" )); workerGroup = new EpollEventLoopGroup(32 , new DefaultThreadFactory("IO_LOOP" )); b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(EpollServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(initializer); public B channel (Class<? extends C> channelClass) if (channelClass == null ) { throw new NullPointerException("channelClass" ); } return channelFactory(new ReflectiveChannelFactory<C>(channelClass)); } final ChannelFuture initAndRegister () Channel channel = channelFactory.newChannel(); }
三、Netty相关参数 1.SO_KEEPALIVE 1 childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true )
TCP链路探活
2.SO_REUSEADDR 1 option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true )
重用处于TIME_WAIT但是未完全关闭的socket地址,让端口释放后可立即被重用。默认关闭,需要手动开启
3.TCP_NODELAY 1 childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true )
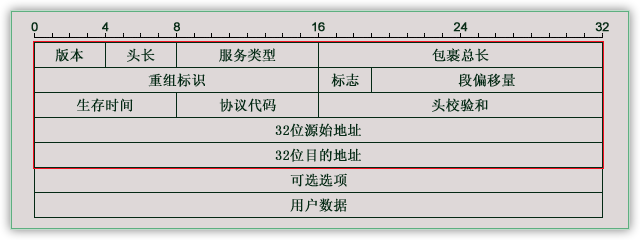
IP报文格式
开启则禁用TCP Negal算法,优点低延时,缺点在大量小数据包的情况下,网络利用率低
关闭则开启TCP Negal算法,优点提高网络利用率(数据缓存到一定量才发送),缺点延时高
Negal算法
如果包长度达到MSS(maximum segment size最大分段长度),则允许发送;
如果该包含有FIN,则允许发送;
设置了TCP_NODELAY选项,则允许发送;
未设置TCP_CORK选项(是否阻塞不完整报文)时,若所有发出去的小数据包(包长度小于MSS)均被确认,则允许发送;
上述条件都未满足,但发生了超时(一般为200ms),则立即发送。
MSS计算规则
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MSS = MTU - IP首部 - TCP首部 以太网环境下: MTU = 1500字节 IP首部 = 32*5/4 = 160bit = 20字节 TCP首部 = 32*5/4 = 160bit = 20字节 最终得出MSS = 1460字节
结论:因为游戏服务器的实时性要求,在网络带宽足够的情况下,建议开启TCP_NODELAY,关闭Negal算法,带宽可以浪费,响应必须及时
注意:需要客户端服务器均关闭Negal算法,否则仍然会有延迟发送,影响传输速度
4.SO_BACKLOG 1 option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100 )
操作系统内核中维护的两个队列
syns queue:保存syn到达,但没完成三次握手的半连接
1 cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog
accpet queue:保存完成三次握手,内核等待accept调用的连接
1 cat /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn
netty对于backlog的默认值设置在NetUtil类253行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 SOMAXCONN = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Integer>() { @Override public Integer run () int somaxconn = PlatformDependent.isWindows() ? 200 : 128 ; File file = new File("/proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn" ); if (file.exists()) { in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); somaxconn = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine()); } else { if (SystemPropertyUtil.getBoolean("io.netty.net.somaxconn.trySysctl" , false )) { tmp = sysctlGetInt("kern.ipc.somaxconn" ); if (tmp == null ) { tmp = sysctlGetInt("kern.ipc.soacceptqueue" ); if (tmp != null ) { somaxconn = tmp; } } else { somaxconn = tmp; } } } } }
结论:Linux下/proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn一定存在,所以backlog一定取得它的值,我参考prod机器的参数配置的65535,也就是不设置backlog的情况下,服务器运行缓存65535个全连接
5.ALLOCATOR和RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR
默认分配ByteBuffAllocator赋值如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 static { String allocType = SystemPropertyUtil.get( "io.netty.allocator.type" , PlatformDependent.isAndroid() ? "unpooled" : "pooled" ); allocType = allocType.toLowerCase(Locale.US).trim(); ByteBufAllocator alloc; if ("unpooled" .equals(allocType)) { alloc = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT; logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: {}" , allocType); } else if ("pooled" .equals(allocType)) { alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT; logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: {}" , allocType); } else { alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT; logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: pooled (unknown: {})" , allocType); } DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR = alloc; }
RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR默认AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class DefaultChannelConfig implements ChannelConfig public DefaultChannelConfig (Channel channel) this (channel, new AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator()); } }
四、Netty关闭 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 Future<?> shutdownGracefully(); Future<?> shutdownGracefully(long quietPeriod, long timeout, TimeUnit unit); static final long DEFAULT_SHUTDOWN_QUIET_PERIOD = 2 ;static final long DEFAULT_SHUTDOWN_TIMEOUT = 15 ;@Override public Future<?> shutdownGracefully() { return shutdownGracefully(DEFAULT_SHUTDOWN_QUIET_PERIOD, DEFAULT_SHUTDOWN_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }
把NIO线程的状态位设置成ST_SHUTTING_DOWN状态,不再处理新的消息(不允许再对外发送消息);
退出前的预处理操作:把发送队列中尚未发送或者正在发送的消息发送完、把已经到期或者在退出超时之前到期的定时任务执行完成、把用户注册到NIO线程的退出Hook任务执行完成;
资源的释放操作:所有Channel的释放、多路复用器的去注册和关闭、所有队列和定时任务的清空取消,最后是NIO线程的退出。